Ontario Animal Health Network (OAHN) Bovine Expert Network Quarterly Producer Report
Surveillance Highlights: Q2 Bovine Animal Health Laboratory Data
There were 156 bovine pathology submissions between May 1st and July 31st 2021 summarized for this quarter.
| Respiratory disease | Pneumonia was the most frequent pathology diagnosis in cattle over 2 months of age. |
| Enteric disease |
Enteritis was the most common diagnosis in young calves (n=5), and the infectious causes were rotavirus, coronavirus, coccidia, cryptosporidium, and Salmonella spp., with concurrent infections identified in several cases. In mature cattle, there was one case of enteritis and embolic hepatitis caused by Salmonella typhimurium. |
| Salmonella | Salmonella Dublin was isolated from 11 samples, representing approximately 6 premises (compared to 6 isolates from 1 premise in Q1). |
| Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus | There were 12 positive test results identified as part of routine herd screening. A total of 310 PCR tests were performed. |
| Toxicosis | Sudden death in 3 dry dairy cows was attributed to ingestion of Yew shrub clippings. Yew (Taxus spp) contain toxic alkaloids which affect the heart resulting in arrhythmia. |


Ontario Bulk Tank SCC Report
Courtesy of Dairy Farmers of Ontario
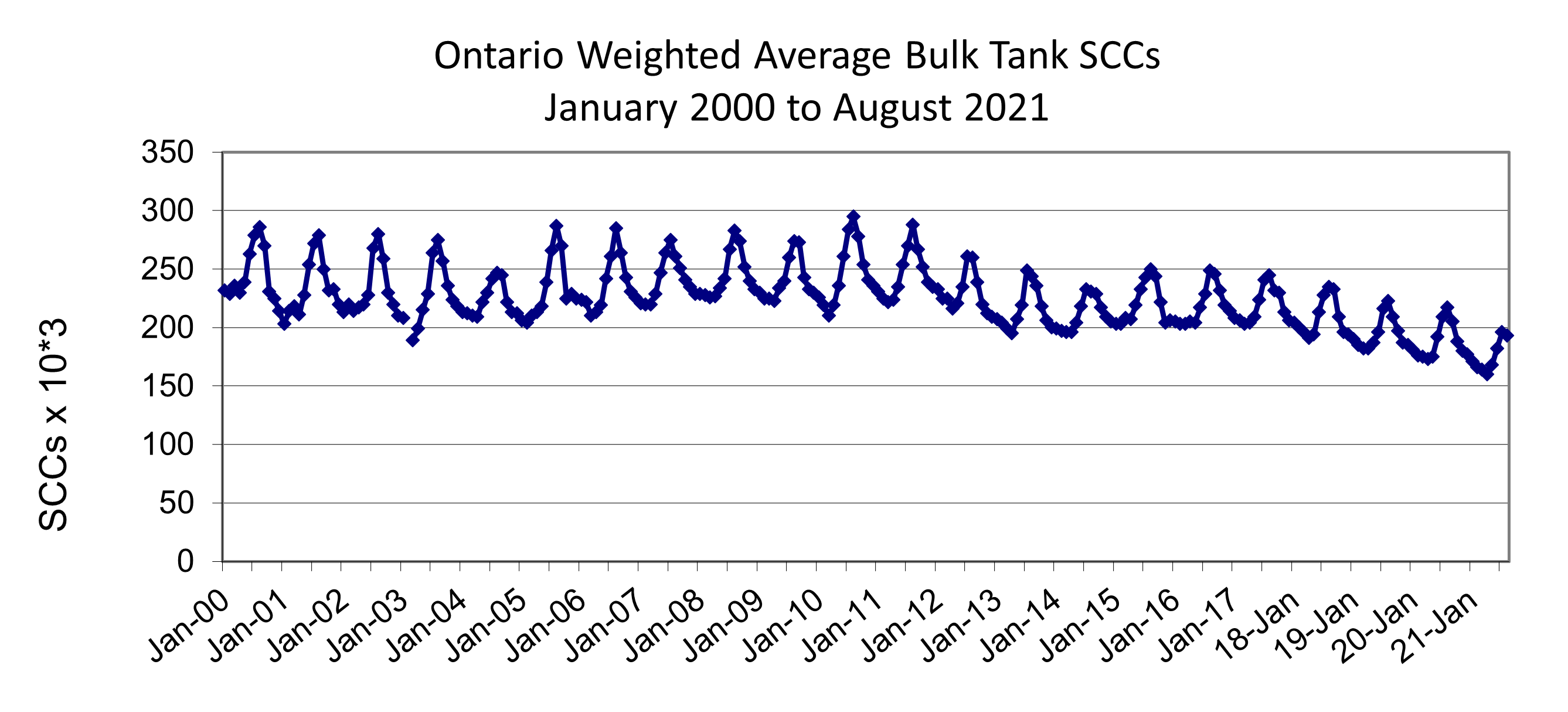
As of August 31, 2021 there were 3,324 licensed milk producers in Ontario.
- The August Bulk Tank Somatic Cell Count (BTSCC) weighted average for Ontario was 193,000 cells/ml.
- The October 2021 Ontario BTSCC was down from 217,000 one year ago!
- The Ontario BTSCC has been below 200,000 in 11 of the last 12 months (October 2020 to August 2021).
New OAHN Podcasts
Bovine Anaplasmosis with Dr. Kathryn Reif
Dr. Kathryn Reif, an assistant professor and researcher at Kansas State University joins the OAHN Bovine network to discuss how to recognize bovine anaplasmosis, how the disease is transmitted, and why the risk to cattle in Ontario might be changing.
Quarterly Report
Get updates from the bovine OAHN team each quarter in at 15 min podcast.
Check them out at https://oahn.podbean.com/category/bovine/
Project Summary: DAIRY
Disease testing for newly introduced cattle
Who:
- 321 dairy cattle ages 2 to 9 years from 56 commercial dairy farms
- Purchased into herd in the last year
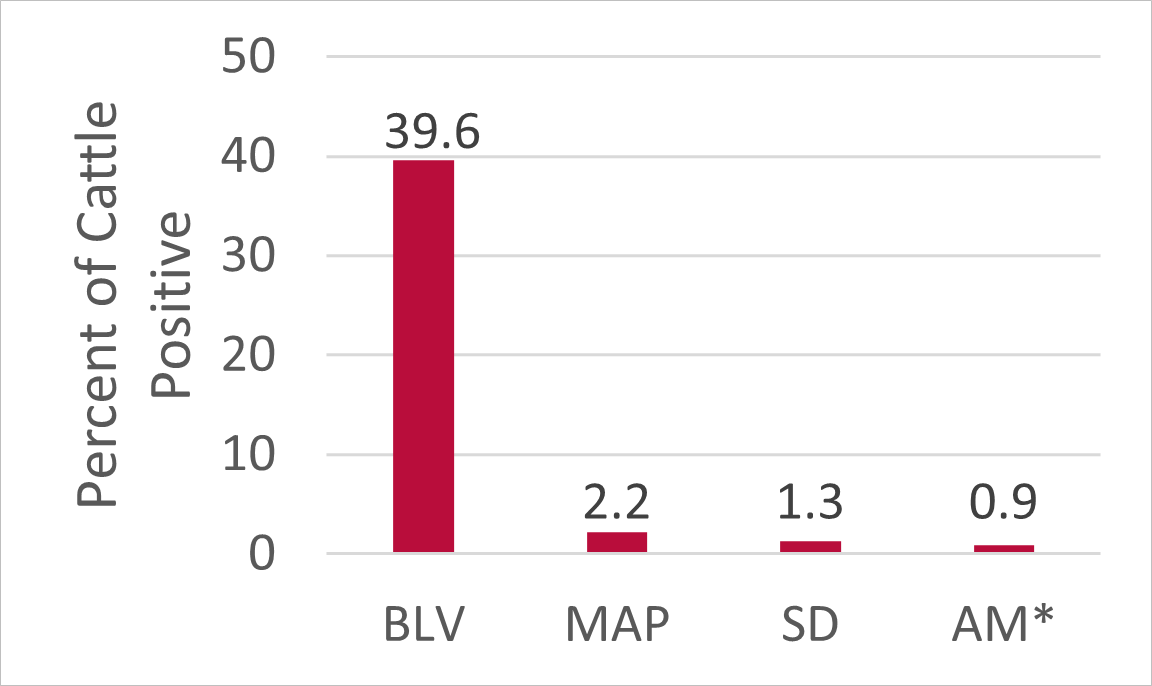
Tested for:
- Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)
- Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis (MAP)
- Salmonella Dublin (SD)
- Anaplasma marginale (AM)
89.7% of farms had purchased cattle within the previous 5 years and most farms (89.4%) had not tested previous purchases for disease.
Results
42.4% of cattle were positive for at least one disease.
 Take Home Message
Take Home Message
- Introducing cattle of unknown health status is a real risk factor for disease entry on Ontario farms
- Veterinarians can inform producers about what testing options are available and review the risk of new purchases as potential vectors for infectious disease
- When purchase is necessary, animals should be sampled prior to addition to the herd to prevent bringing infectious diseases onto their farm. If not feasible, animals should be tested immediately after introduction to the herd and managed to minimize transfer of pathogens.
- No test is perfect – knowing the herd of origin and inquiring about their disease status reduces the risk of introducing infectious diseases with new purchases
Project Summary: BEEF
Disease testing for newly introduced cattle
Who:
- 31 beef cattle ages 2.5 to 5 years from 5 commercial beef farms
- Purchased into herd in the last year
Tested for:
- Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)
- Mycobacterium avium subsp. Paratuberculosis (MAP)
- Salmonella Dublin (SD)
- Anaplasma marginale (AM)
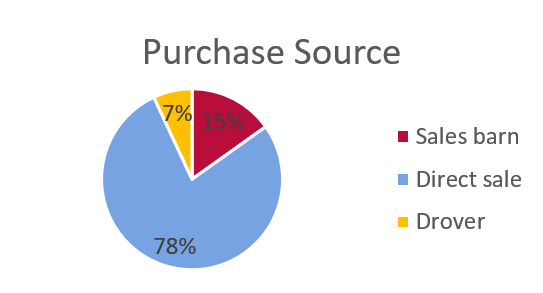
Purchase Source
- 18 cattle were purchased within Ontario
- 13 cattle were purchased from outside of Ontario, including 9 from USA
Results:
- Only a small number of beef cattle were tested as part of the project therefore results cannot be applied to all beef cattle in Ontario
- 35% (11/31) of beef cattle were positive for BLV
- 2 cattle purchased from the USA were positive for anaplasmosis and had active infection (positive PCR test)
Take Home Messages
- The risk of disease in purchased beef cattle in Ontario and purchase practices remains undetermined
- Cattle from out-of-country can be a risk for introduction for diseases not commonly found in Canada such as bovine anaplasmosis.
- A younger age at time of purchase may have limited the detection ability and therefore usefulness of the MAP ELISA test in beef cattle in the project
- Knowing the herd of origin, sampling newly purchased animals, and managing cattle to minimize transfer of pathogens until status is known are best practices for purchasing cattle
New Salmonella Dublin Resources

Salmonella Dublin is an emerging threat in cattle across Canada. The OAHN bovine network highlights laboratory cases quarterly and annually to keep producers and veterinarians aware of the risk.
The OAHN bovine network is very pleased to highlight new resources available for producers and veterinarians produced by Veal Farmers of Ontario.
The available resources include 5 factsheets, 4 case studies, and a podcast and cover how to recognize Salmonella Dublin, human health impacts, prevention and control and much more.
Check them out at: http://calfcare.ca/salmonella-dublin


